Welcome: Shenzhen Limei Technology Co., Ltd
Email: szlimei@tddfdd.com
- TOP
- 13025463935
- Online
- WhatsApp code

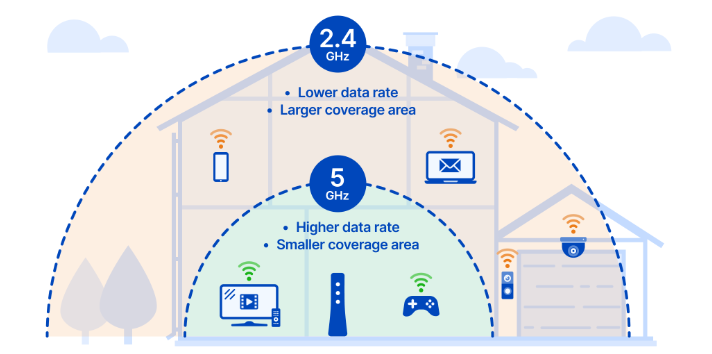
Aspect
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
Frequency Range
2.4000 GHz - 2.4835
GHz
5.150 GHz - 5.825
GHz
Interference
Susceptible to
interference from devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth
devices
Less crowded
spectrum, lower likelihood of interference
Range
Longer range, better
at penetrating obstacles like walls and physical barriers
Shorter range, may
be affected by obstacles more easily
Data Transfer Speed
Slower compared to 5
GHz
Faster speeds, ideal
for bandwidth-intensive activities like HD video streaming and gaming
Device Compatibility
Widely supported by
most devices
Support varies, some
older devices may not be compatible
Network Congestion
More susceptible to
network congestion due to a crowded spectrum
Less congestion,
higher number of available channels
Contact: Sorho
Phone: +8613025463935
Email: szlimei@tddfdd.com
Add: 1006, 10th Floor, Shajing Yunhua Times Building, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China